The National Pension System (NPS) is a long-term retirement-focused investment product backed by the Government of India. Initially introduced in 2004 for government employees, NPS was opened to all Indian citizens in 2009. Since then, NPS has emerged as a reliable savings tool to build a secure retirement corpus.
What is the National Pension System (NPS)?
NPS is a voluntary, defined-contribution retirement savings scheme. You contribute a portion of your income regularly into your NPS account throughout your working life. Upon reaching the age of 60, you can withdraw up to 60% of the total NPS corpus as a tax-free lump sum, while the remaining 40% must be used to purchase an annuity that provides a monthly pension.
Earlier, only 40% of the lump sum NPS corpus was exempt from tax. But now, 60% of the NPS corpus withdrawal is tax-free, making NPS an even more attractive option for retirement planning.
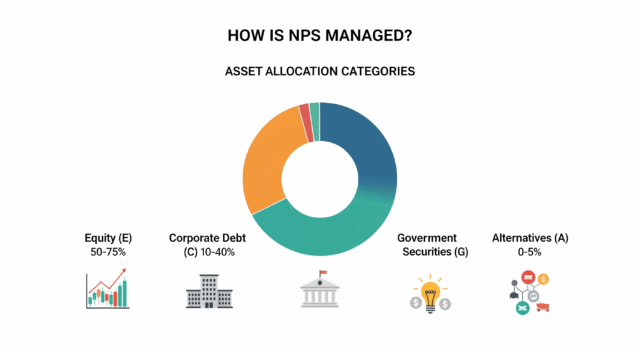
How is NPS Managed?
The Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) oversees the functioning of NPS. The NPS scheme offers investment in the following asset classes:
-
Equity (E): Invests predominantly in equity markets.
-
Corporate Debt (C): Includes bonds issued by PSUs, public financial institutions, and infrastructure companies.
-
Government Securities (G): Comprises bonds issued by central and state governments.
-
Alternative Investment Funds (A): Covers instruments like REITs, InvITs, and other alternative assets.
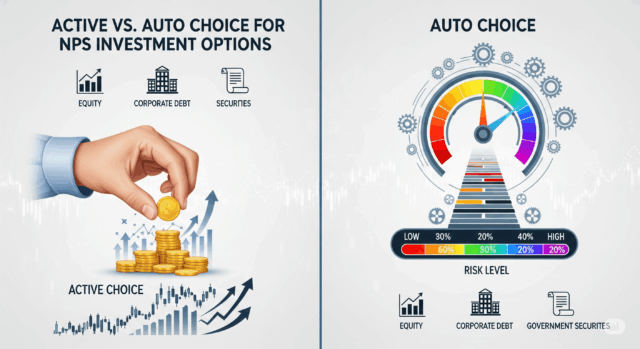
NPS Investment Options
Subscribers of NPS can choose between two investment strategies:
Active Choice in NPS:
-
You control your asset allocation.
-
Equity investment is capped at 75%, while corporate debt and government securities can go up to 100%.
-
After age 50, equity exposure reduces by 2.5% each year.
Auto Choice in NPS:
-
A lifecycle-based NPS investment strategy.
-
Starts with a higher equity allocation and gradually shifts to safer assets like debt and government bonds as you approach retirement age.
Your risk appetite plays a vital role in choosing between these two NPS options. Aggressive investors may prefer the active choice, while those unsure about managing their asset allocation might find the auto choice more suitable.
Who is Eligible to Join NPS?
Any Indian citizen between the ages of 18 and 65 can open an NPS account, provided they comply with KYC (Know Your Customer) norms.
Can NRIs Invest in NPS?
Yes, Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) can also invest in the NPS. Here’s how they can do it:
-
Must hold a PAN card and have a bank account with an NPS-registered bank.
-
Can open an NPS account online via the PFRDA/NPS Trust portal.
-
Must choose between Repatriable or Non-Repatriable account types.
-
Provide details like PAN, passport number, and country of residence.
-
Upload a scanned photograph and signature.
-
An initial contribution of Rs. 500 is required.
-
After registration, the NPS subscriber must send a signed physical copy of the application form to the Central Record Keeping Agency (CRA) within 90 days.
Maximum Age to Join and Contribute to NPS
The maximum age to join NPS has now been extended to 65 years (earlier it was 60). NPS subscribers can continue investing till the age of 70. This extension aims to include a wider population under the NPS scheme.
Who Should Invest in NPS?
Given that India lacks a universal social security system, NPS is a prudent choice for anyone looking to build a retirement fund. Whether you’re a government employee, a private sector professional, or even self-employed, investing early in NPS helps in:
-
Building a sizeable NPS retirement corpus
-
Benefiting from long-term compounding through NPS
-
Reducing tax liabilities under the old tax regime via NPS
Types of NPS Accounts
There are two types of NPS accounts:
Tier I NPS Account:
-
A mandatory NPS retirement account with restrictions on withdrawals.
-
Offers tax benefits and is designed to serve long-term retirement goals.
Tier II NPS Account:
-
A voluntary NPS savings account.
-
Offers more flexibility with withdrawals but no tax benefits.
-
Can be opened only if you have an active Tier I NPS account.
How Does NPS Work?
NPS is a defined contribution scheme where your contributions are invested as per your selected asset allocation strategy (Active or Auto).
-
At retirement (age 60), you can withdraw 60% of the total NPS corpus tax-free.
-
The remaining 40% must be used to purchase an annuity plan from a PFRDA-approved insurance provider, which then offers a monthly pension.
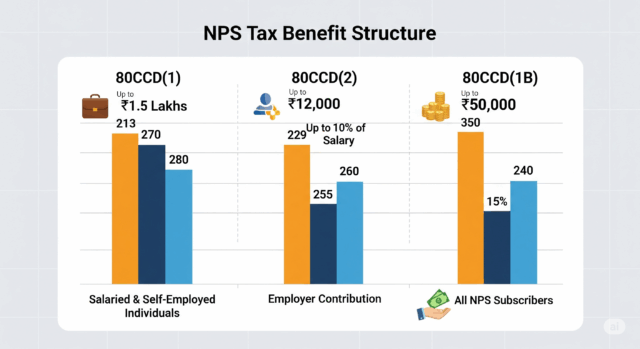
Tax Benefits of NPS
NPS provides tax deductions under the following sections:
-
Section 80CCD(1): Deduction up to Rs. 1.5 lakh (within the overall limit of Section 80C).
-
Section 80CCD(2): Additional deduction for employer’s contribution (up to 10% of salary – Basic + DA), with no upper limit.
-
Section 80CCD(1B): Additional Rs. 50,000 deduction, over and above the Rs. 1.5 lakh limit under Section 80C.
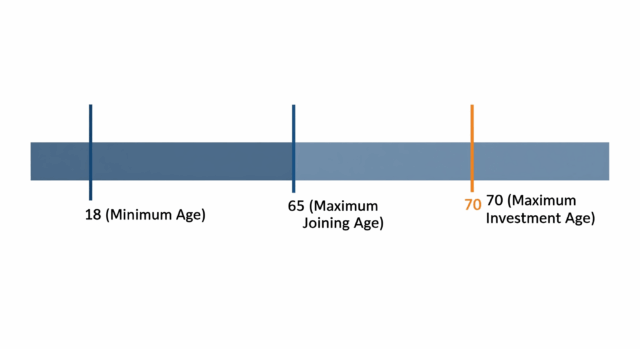
Minimum and Maximum Age Criteria for NPS
-
Minimum age to start investing in NPS: 18 years
-
Maximum age to start investing in NPS: 65 years
-
NPS investment can continue till: 70 years
Final Thoughts on NPS
The National Pension System (NPS) has evolved significantly over the years, making it a reliable and tax-efficient tool for retirement planning. Its long lock-in period ensures disciplined savings, and the power of compounding through NPS helps grow your wealth substantially. With its low-cost structure, flexible investment options, and tax benefits, NPS is suitable for anyone aiming to build a financially secure post-retirement life.
Whether you’re a salaried individual, a self-employed professional, or an NRI, investing in NPS today can pave the way for a stress-free retirement tomorrow. NPS is not just an investment—it’s your future safety net.